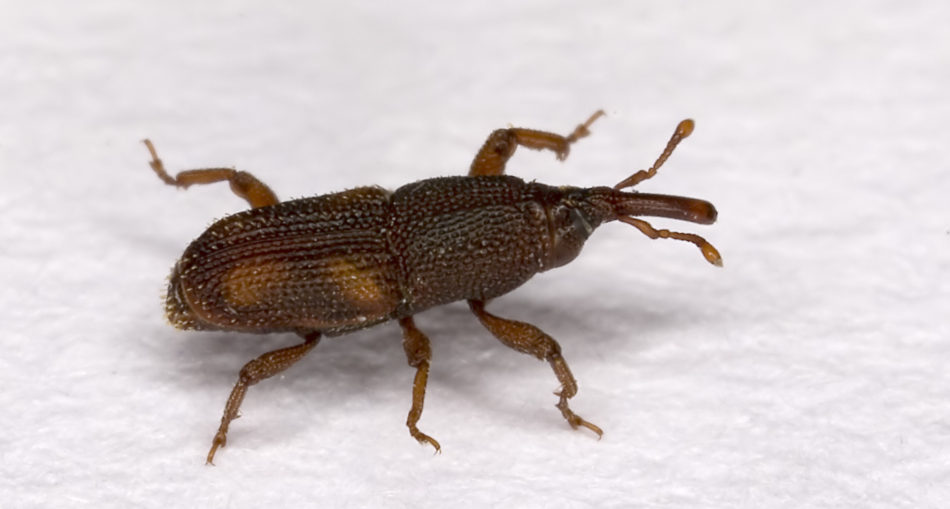
Have you ever opened a bag of rice just to find one of these tiny, tick-like insects crawling around? You might have even tried to catch it, burying your hand beneath grains of rice just to be outwitted by something that is literally the size of a rice grain. These insects are known as ‘Rice Weevil‘.
Scientific Classification
Scientific name: Sitophilus oryzae
Higher classification: Sitophilus
Rank: Species
Order: Coleoptera
Family: Curculionidae
Phylum: Arthropoda
Kingdom: Animalia
Description
Adult weevils range in size from 2-3 millimeters. The mature rice weevil is a dull reddish-brown to black color, with four pale reddish or yellowish patches on the elytra (forewings) and round or irregularly formed pits on the thorax (wing covers). The mature weevil has the ability to fly and is drawn to lights. The larvae of rice weevils are white to a creamy white colour, they are legless with a small tan head.
Habitat
Rice weevils are usually found in grain storage facilities or processing plants, infesting wheat, oats, rye, barley, rice, and corn. Rice weevils prefer tropical or subtropical environments.
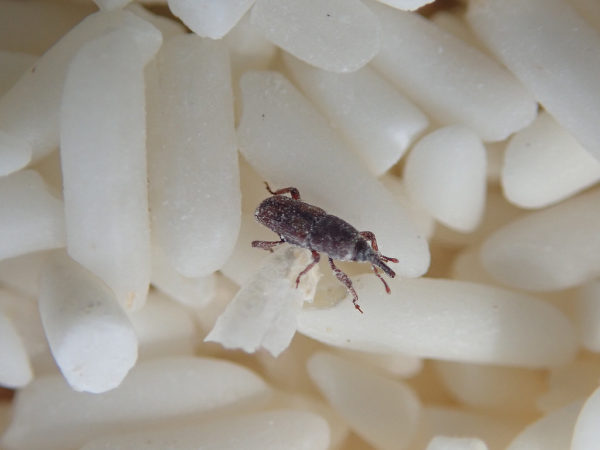

Rice weevil on rice. Photo Source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/jacobs_ian/42368875970
Diet
Rice weevils have chewing mouthparts that allow them to feed on grains such as corn, oats, barley, and, of course, rice.
Reproduce
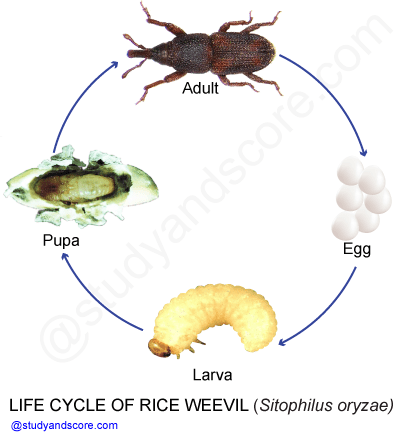
Lifecycle of rice weevil. Photo Source: https://www.studyandscore.com/studymaterial-detail/pest-of-rice-sitophilus-oryzae-distribution-life-cycle-nature-of-damage-and-control-measures
Females can lay 300 to 400 eggs typically one per cavity. Larvae develop through several stages (instars) inside the grain kernels and also pupate inside the kernel. They may complete a generation in a month in warm conditions. Adults often live for 7 to 8 months and some records are over 2 years.
Damages Caused By Rice Weevil
Rice weevils are no harm to human beings, however, they are a rice farmer’s worst enemy. The larvae of rice weevils tend to hollow out kernels of grain and also feed on the roots which cause stunted growth and chlorosis (the yellowing of leaves), this makes it easy for plants to be uprooted. The adults feed on leaves and leave behind slit-like leaf scars which is not an issue for fully grown plants but when they feed on younger plant leaves it can destroy the entire plant.
How To Control Rice Weevil Infestation
- Sampling activity should be done one week after permanent flooding. Inspect 100 randomly selected leaves and if 50 and above have feeding scars apply insecticide (Fastac, Pestac, Karate, or Pronto).
- Control is most effective 7-14 days after a permanent flood when weevil numbers are at or above the economic threshold level.
- Control of larvae can be done by draining the field and allowing it to dry until it cracks.
- Good field sanitation will get rid of alternative weed hosts.
Good Field Sanitation Includes:

Image showing a girl pulling out infected plants. Photo source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/asiandevelopmentbank/19758378852
- Keep weeds under control at all times and maintained them.
- Pull out any infected plants.
- The crop remains and organic mulches should be plowed beneath. This enhances soil quality and aids in breaking the pest’s life cycle. Pests are subjected to high temperatures, mechanical damage, and predators.
- Make your own compost. Your compost pile is where you can place your plant trimmings and other plant debris.
- Clean your farm tools. Wash ploughs, harrows, shovels, trowels, and pruning gears after use. Lightly oil pruning gears.
References:
- Description: https://extension.okstate.edu/programs/digital-diagnostics/insects-and-arthropods/rice-weevil-sitophilus-oryzae/
- (https://extensionentomology.tamu.edu/insects/rice-weevil/
- https://www.grainscanada.gc.ca/en/grain-quality/manage/identify-an-insect/primary-insect-pests/rice-weevil.html
- Controlling a Rice Weevil Infestation: https://grdb.gy/entomology/#:~:text=Larvae%20feed%20on%20the%20roots,referred%20to%20as%20%E2%80%9Cwindowing%E2%80%9D
- Good Field Sanitation: https://infonet-biovision.org/PlantHealth/Field-sanitation
Discover more from Things Guyana
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.







